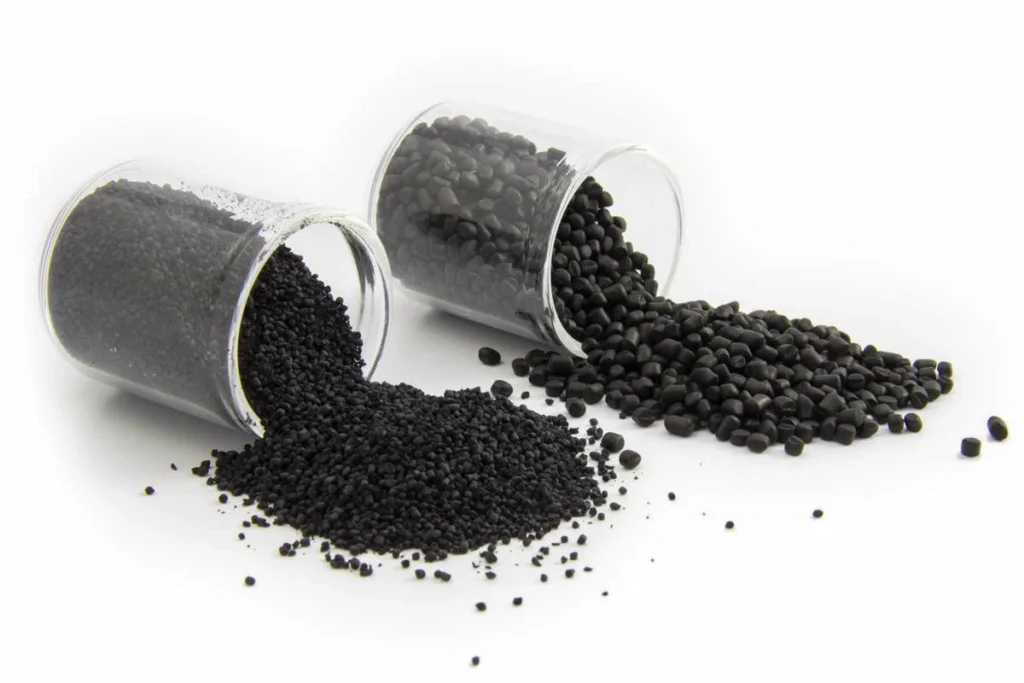
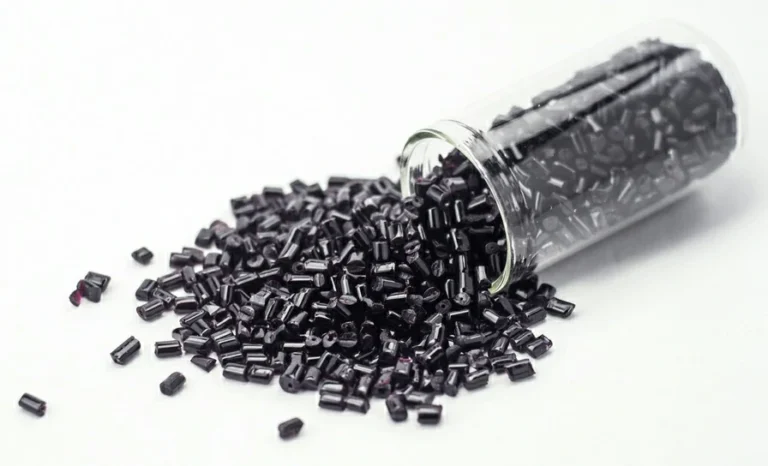
Conductive masterbatch is a high-concentration functional masterbatch made by adding conductive fillers to a polymer resin carrier. By uniformly dispersing conductive materials (such as carbon black, metal powders, conductive fibers, etc.) within the polymer matrix, it enhances the electrical conductivity of plastic products. It is widely used in industries requiring antistatic properties and electrical conductivity, including electronics, communications, and automotive. First, let’s examine the composition of conductive color masterbatch.

What is Conductive Masterbatch Made of?
The composition of conductive colour masterbatch primarily consists of three components: carrier, conductive filler, and functional additives.
Polymer Carrier: Typically employs carrier resins like PE, PP, PET, or ABS. This component carries the conductive filler while ensuring processing compatibility and flow properties for the masterbatch.
Conductive Filler: Commonly carbon black, carbon fiber, metal powder, or conductive polymers are used to establish conductive pathways, achieving surface or bulk conductivity.
Functional Additives: Including dispersants, flow agents, and antioxidants, these improve the dispersion of conductive fillers within the carrier, enhance processing performance, and ensure long-term stability.
Through optimized formulation, conductive colour masterbatches deliver stable conductivity across diverse plastic systems while maintaining excellent processability and visual appearance. Next, let’s examine how conductive masterbatches work.
Working Principle of Conductive Masterbatches
The mechanism primarily relies on the dispersion and interaction of conductive fillers within the matrix resin. Conductive fillers—such as carbon black, metal powders, and conductive fibers—are substances possessing electrical conductivity. When uniformly dispersed within the polymer matrix, these fillers come into mutual contact, forming conductive pathways. At sufficient filler concentrations, physical contact establishes conductive routes. Overall, conductive fillers connect via electrical conductivity to form a continuous three-dimensional conductive network. Under an external electric field, electrons can freely move within this network to conduct current. Having understood the working principle of conductive masterbatch, let’s explore its application fields.

Applications of Conductive Masterbatches
Conductive color masterbatches offer excellent antistatic and conductive properties, making them widely used in various plastic products, primarily across these major sectors:
Electronic and Electrical Enclosures: Used in phone cases, computer housings, power supply casings, etc., to prevent static damage to internal electronic components.
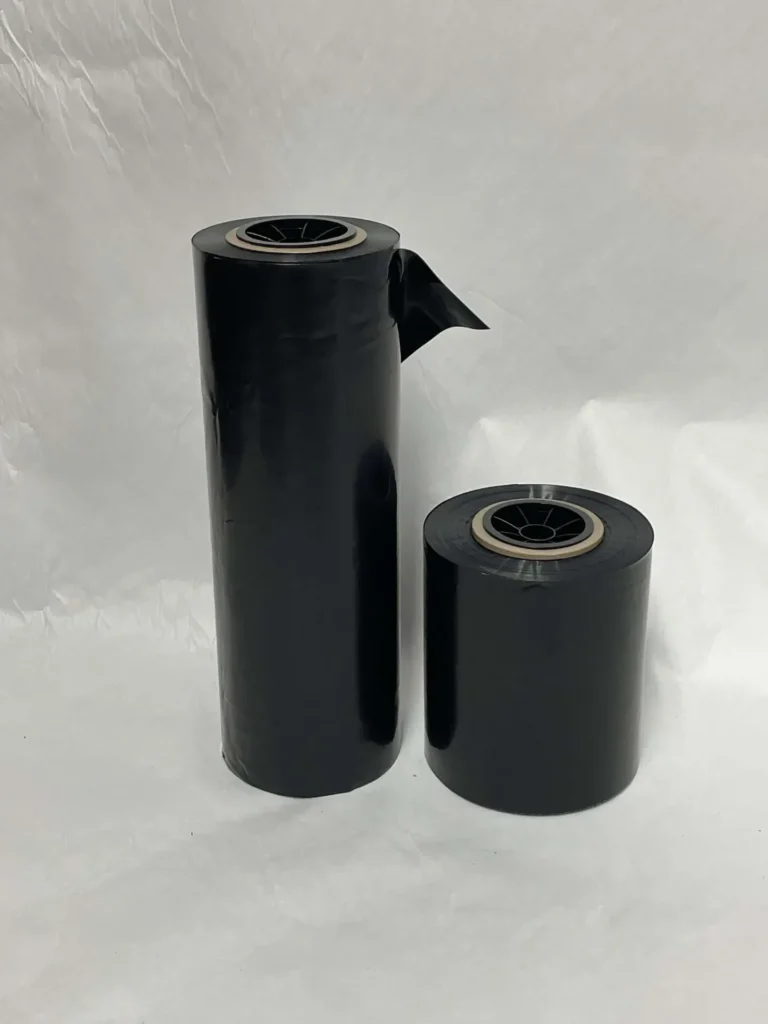
Plastic Packaging Materials: Commonly incorporated into PE/PP films, roll films, and bags to prevent dust adhesion and static buildup.
Precision Instruments and Medical Devices: Employed in static-sensitive equipment like displays, sensors, and medical syringes requiring long-term stable conductivity.
Automotive and Transportation Components: Frequently used in automotive interior parts, dashboards, and fuel system components to reduce static risks and enhance safety.
Electrostatic-sensitive industrial products: Employed in anti-static flooring, conductive pipe fittings, and similar applications across electronics, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Given the broad applicability of conductive master batch, how should purchasers select the appropriate product? What factors require consideration?
How to choose the right conductive masterbatch
When selecting an appropriate conductive color master batch from a buyer’s perspective, the following key factors should be considered:
Conductivity Requirements: Determine the required conductive properties based on the application scenario. For example:
- Anti-static: Typically requires low conductivity, suitable for electronic devices, packaging, etc.
- High Conductivity: For electromagnetic shielding (EMI) or high-frequency electronics, select masterbatches with enhanced conductivity (e.g., metal powder fillers).
Application Field:
- Industrial Use: Applications like automotive components or electronic enclosures require masterbatches with excellent conductivity, temperature resistance, and abrasion resistance.
- Medical or Food Packaging: Prioritize non-toxicity and environmental compliance, ensuring adherence to relevant safety standards.
Processing Requirements:
- Flowability: Selected conductive masterbatches must process smoothly during injection molding, extrusion, and other production processes. If processing equipment has specific flow requirements, choose masterbatches with high flowability.
- Dispersibility: Uniform dispersion of conductive fillers affects electrical conductivity. Verify masterbatch dispersibility meets standards during selection.
Temperature Resistance and Stability: For high-temperature environments, select thermally stable conductive masterbatches to prevent material degradation at elevated temperatures. Consideration should also be given to other factors, such as maintaining UV resistance and oxidation resistance.
Cost and Budget: Select products within budget constraints. High-conductivity fillers command higher prices, while options like carbon black offer greater cost-effectiveness. A balance between performance and cost should be achieved.
High Quality Suppliers: Choose suppliers with a strong reputation and quality control systems. Verify their ability to provide technical support, quality assurance, and stable supply with reliable after-sales service to foster long-term partnerships.

Conclusion
Through the above article, we have learned about the composition, principles, and selection criteria of conductive color masterbatches. We understand that they effectively prevent static electricity, reduce dust adhesion, and enhance the safety and user experience of plastic products. If you require conductive masterbatches, please contact us. Huashuo is a masterbatch manufacturer with a professional service team that can provide customized solutions tailored to your production needs.