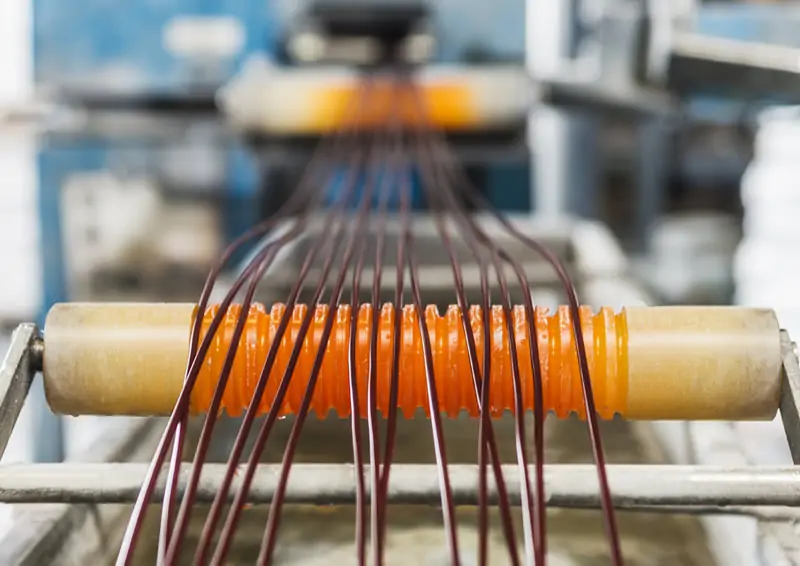
Filler masterbatch is one of the most commonly used functional additives in the plastics industry. It is typically produced through a series of processes, including mixing and blending of fillers, carriers, and additives in specific proportions, followed by melting, extrusion, cooling, pelletizing, screening, and packaging to create the final product. It is widely favored by manufacturers for its ability to reduce production costs, alter functional properties, and optimize production equipment. The application of Filler Masterbatch spans nearly the entire plastic industry chain, including packaging, daily necessities, and the automotive industry. Let’s take a closer look at the specific functions of Filler Masterbatch.
What are the functions of Filler Masterbatch?
Filler Masterbatch excels in the following areas, which are the primary reasons for its popularity among manufacturers:
Production costs: This is the most significant function. The primary components of Filler Masterbatch (such as calcium carbonate and talc) are significantly cheaper than plastic resins themselves. By scientifically blending and adding these components, manufacturers can reduce the use of expensive resins while maintaining the basic performance of the product, thereby significantly lowering raw material costs.
Modifying product performance: Different types of Filler Masterbatch can impart specific performance changes to plastic products:
For example, adding talc masterbatch enhances the rigidity and heat resistance of the product;
adding calcium carbonate masterbatch improves dimensional stability, increases opacity, and enhances whiteness;
special functional masterbatches (such as flame-retardant or conductive masterbatches) can impart new properties to plastics.
Optimizing production equipment and processes:
Granular masterbatches have good flowability and mix uniformly with raw resin, avoiding dust contamination issues associated with direct use of powdered fillers.
Masterbatches typically contain dispersants and lubricants, which improve the flowability of the plastic melt, making the processing smoother, increasing production efficiency, and reducing wear on production equipment.
What are the types of filler masterbatches?
The types of filler masterbatches are primarily classified based on their core filler components and the carrier resin used:
By primary filler type:
CaCO₃ masterbatch: The most commonly used and cost-effective filler masterbatch, primarily used to reduce costs, enhance rigidity and dimensional stability, and increase opacity. It is available in heavy calcium carbonate (HCC) and light calcium carbonate (LCC) formulations.
Talc masterbatch: Significantly improves the rigidity, heat resistance, and surface hardness of plastics (especially polypropylene PP), widely used in automotive components, appliance housings, and other applications.
Barium sulfate masterbatch: Primarily used to increase the density and specific gravity of products, it offers excellent X-ray shielding properties and is commonly used in medical and audio components.
Other functional filler masterbatches: Such as mica masterbatch (enhances heat resistance and dimensional stability), diatomite masterbatch (reinforcing), kaolin masterbatch, and glass microsphere masterbatch (reduces density and improves dimensional stability), etc.
Classified by carrier resin type:
Polyolefin carrier masterbatch (PP/PE): The most common type, with the carrier typically being LDPE or LLDPE, used for filling polyolefin plastic products such as PP, PE, and HDPE.
PVC carrier masterbatch: Specifically designed for filling and modifying PVC plastic products.
Engineering plastic carrier masterbatch: Such as specialized filler masterbatch for engineering plastics like PA, PC, and PBT, which have higher compatibility requirements.
Applications of Filler Masterbatch in Various Industries
Filler masterbatch has extremely widespread applications, penetrating nearly every corner of the plastic industry chain. The following are some major application industries and typical products:
Packaging industry: This is one of the largest application areas for filler masterbatch.
Examples include: plastic woven bags, bulk bags, packaging films, bottles, drums, pallets, packaging straps, sheets, and foam packaging materials.
Household goods industry: A large number of daily plastic products use Filler Masterbatch to reduce costs.
Examples include: basins, buckets, chairs, coat hangers, trash cans, food storage containers, tableware, children’s toys, and sanitary ware components.
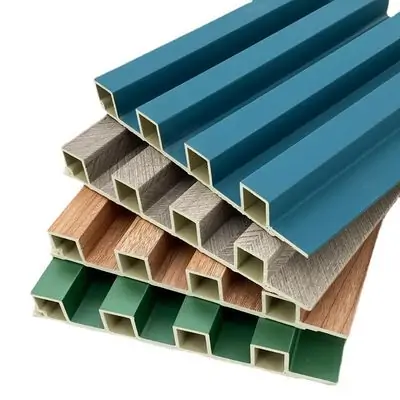
Construction materials industry: This sector has high requirements for cost control and performance (such as rigidity and weather resistance).
Examples include: pipes (PPR pipes, PVC drainage pipes), fittings, profiles (door and window profiles), panels (ceiling panels, partition panels), composite wood (plastic wood), and foam building materials, etc.
Automotive industry: Primarily utilizes Filler Masterbatch (particularly talc-reinforced PP) to achieve lightweighting and performance enhancement.
Examples: Bumper, dashboard, door panels, interior trim, mudguards, fan covers, battery casings, etc.
Agricultural sector: Emphasizes cost-effectiveness and durability.
Examples: Agricultural mulch film, irrigation pipes, seedling trays, pesticide packaging drums, etc.
Wires and cables: Used in cable sheathing materials, etc., to reduce costs and improve specific performance.
Other industrial fields: Such as appliance housings, industrial components, logistics pallets, etc.
Conclusion
Through the above introduction, I believe you now understand what filler masterbatch is and are aware of its functions and advantages. If you are a manufacturer in the plastics industry and are struggling with high costs for color and products, please contact us immediately. We are a professional manufacturer of color masterbatch, with a dedicated service team to provide you with professional solutions for your production needs.